Current and planned energy infrastructure could emit around 850 gigatons of the greenhouse gas.
A new study shows just how hard it may be to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius over preindustrial times.
The world’s existing power plants, industrial equipment, vehicles and other CO₂-emitters are on track to pump out enough carbon dioxide to blow past that target by midcentury, researchers report July 1 in Nature. Add in future power plants that are already planned, permitted or under construction, and we could emit enough by 2033 to raise average global atmospheric temperatures by 1.5 degrees, the researchers say.
If we want to limit warming to 1.5 degrees, then “we cannot invest more in fossil fuel power or infrastructure,” says Thorsten Mauritsen, a physical climate scientist at Stockholm University who was not involved with the work. “Everything we do from now has to change direction and not use fossil fuels.”
In the 2015 Paris Agreement on climate change, nearly all the world’s nations agreed to try to reduce greenhouse gas emissions enough to limit warming to “well below” 2 degrees by 2100 (SN: 1/9/16, p. 6). The United States has said it would pull out of the agreement (SN Online: 6/1/17), though the exit wouldn’t be complete until 2020.
Still, calls have increased since 2015 for the more ambitious goal of keeping warming to 1.5 degrees. That would mean fewer heat waves, spells of extreme weather and species extinctions (10/27/18, p.7).

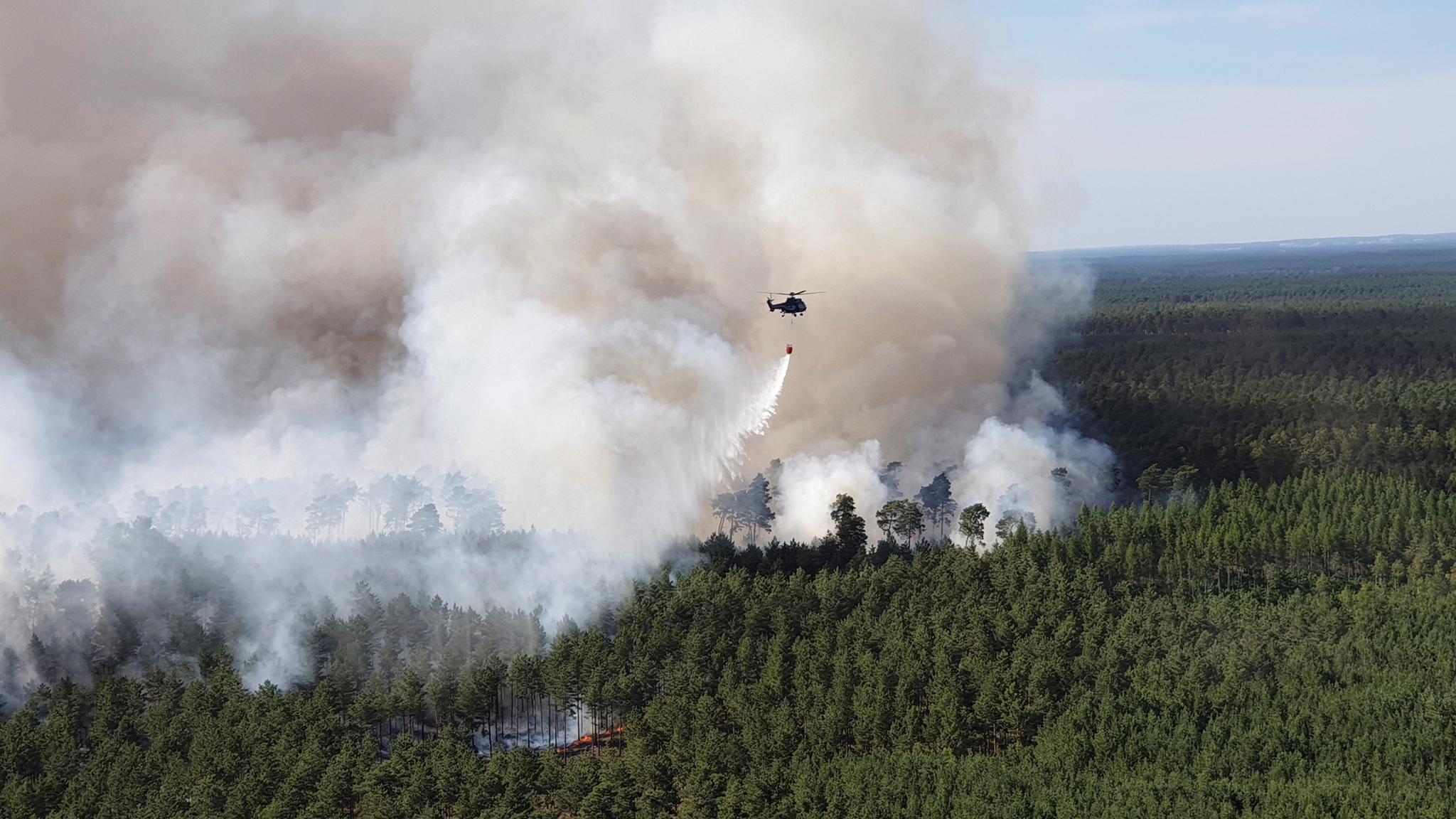
COMMITTED Carbon dioxide emissions from the fossil fuel infrastructure that’s already built will probably push us past 1.5 degrees Celsius of global warming, according to a new study.
Continue reading at: CO2 emissions are set to exceed 1.5 degrees of global warming | Science News
A new study shows just how hard it may be to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius over preindustrial times.
The world’s existing power plants, industrial equipment, vehicles and other CO₂-emitters are on track to pump out enough carbon dioxide to blow past that target by midcentury, researchers report July 1 in Nature. Add in future power plants that are already planned, permitted or under construction, and we could emit enough by 2033 to raise average global atmospheric temperatures by 1.5 degrees, the researchers say.
If we want to limit warming to 1.5 degrees, then “we cannot invest more in fossil fuel power or infrastructure,” says Thorsten Mauritsen, a physical climate scientist at Stockholm University who was not involved with the work. “Everything we do from now has to change direction and not use fossil fuels.”
In the 2015 Paris Agreement on climate change, nearly all the world’s nations agreed to try to reduce greenhouse gas emissions enough to limit warming to “well below” 2 degrees by 2100 (SN: 1/9/16, p. 6). The United States has said it would pull out of the agreement (SN Online: 6/1/17), though the exit wouldn’t be complete until 2020.
Still, calls have increased since 2015 for the more ambitious goal of keeping warming to 1.5 degrees. That would mean fewer heat waves, spells of extreme weather and species extinctions (10/27/18, p.7).

COMMITTED Carbon dioxide emissions from the fossil fuel infrastructure that’s already built will probably push us past 1.5 degrees Celsius of global warming, according to a new study.
Continue reading at: CO2 emissions are set to exceed 1.5 degrees of global warming | Science News